Nikon Announces New Image Analysis Functions to Empower Drug Discovery Research for Cancer, Neurological Disease, and Regenerative Medicine
New software updates bring expanded capability to the ECLIPSE Ji smart imaging system
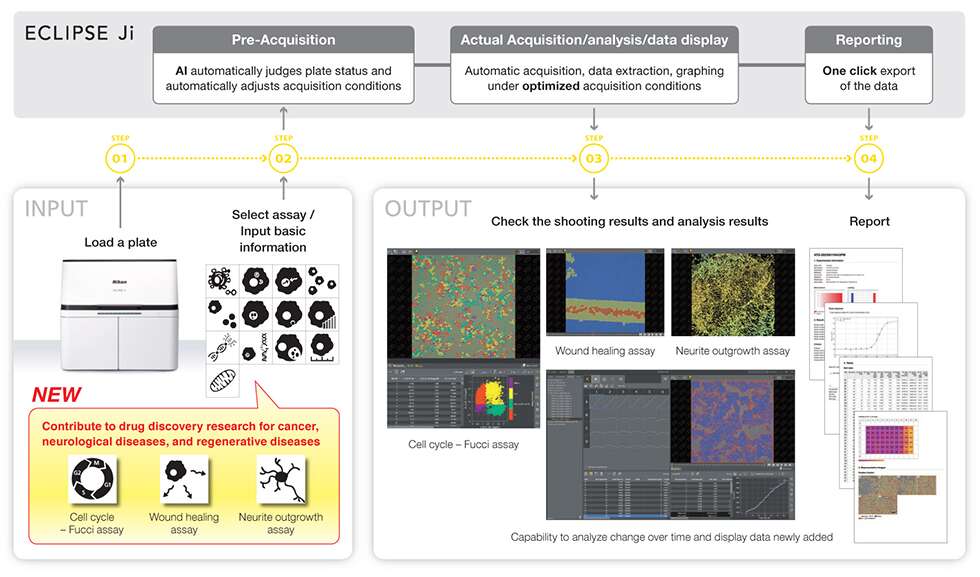
MELVILLE, NY – Nikon Instruments Inc. (Nikon) is pleased to announce a new software update for the ECLIPSE Ji smart imaging system (compatible with NIS-Elements ver. 6.10 onward) that brings a variety of broadened experimental capabilities to areas such as oncology, neurology, and regenerative medicine. The update will be available beginning August 30.
A wide range of experimental protocols are needed for basic research and drug candidate evaluation in oncology and neurology. In recent years, companies engaged in drug discovery research and development have also sought improved experimental efficiency, simplified operations, increased scalability, and high-speed screening capabilities. The ECLIPSE Ji smart imaging system is currently equipped with thirteen assays1 designed to quantitatively assess a diverse set of cellular characteristics with a high degree of repeatability. This software update adds three new assays for applications in oncology, neurology, and regenerative medicine. In addition, new time-lapse imaging capabilities that evaluate and report changes over time are added to certain pre-existing assays to enable more advanced experiments.
This update will assist research institutions, biotechnology companies, and organizations engaged in drug discovery research and development in efficiently capturing and analyzing complex cellular responses to novel treatment technologies. It will streamline the drug discovery process in areas such as oncology, neurology, and regenerative medicine.
Nikon continues to develop products that take advantage of its renowned microscopy technologies while simultaneously addressing customer needs in order to empower drug discovery research and development. Nikon continues to strive to offer solutions that contribute to the elucidation of disease mechanisms and the acceleration of new drug development.
1 A type of experiment in which biological materials, such as cultured cells, are used to evaluate functional activities and reactions.
Release Overview
| Product Version | Software: NIS-Elements ver. 6.10, for the ECLIPSE Ji |
|---|---|
| Release Date | August 30, 2024 |
| Major Updated Items | 1. Addition of 3 new assays
• Cell Cycle – Fucci 2. Time-lapse capability for existing assays
|
Major Features of the Update
The ECLIPSE Ji is a smart imaging system that combines highly accurate image analysis with easy-to-use assisted image acquisition. It can automatically optimize imaging conditions, perform imaging acquisition and analysis, display interactive data, and generate reports simply by setting the specified samples for imaging on the device and following the on-screen instructions. This update adds three new assays to the existing set of thirteen, aiming to further contribute to the fields of oncology, neurology, and regenerative medicine.
1. Automated analysis to evaluate cancer cell division and proliferation
Cell cycle assays are in high demand for the study of cancer cells with significant proliferative potential. By observing fluorescent proteins that change color according to specific stages of the cell cycle, automated analysis can be used to track cell cycle stages for each cell individually to study the effects of new drugs on cellular division.
The wound healing assay is designed to assess the changing cellular coverage of induced wound sites over time, or the infiltration of inflammatory sites in cancer cell invasion studies.
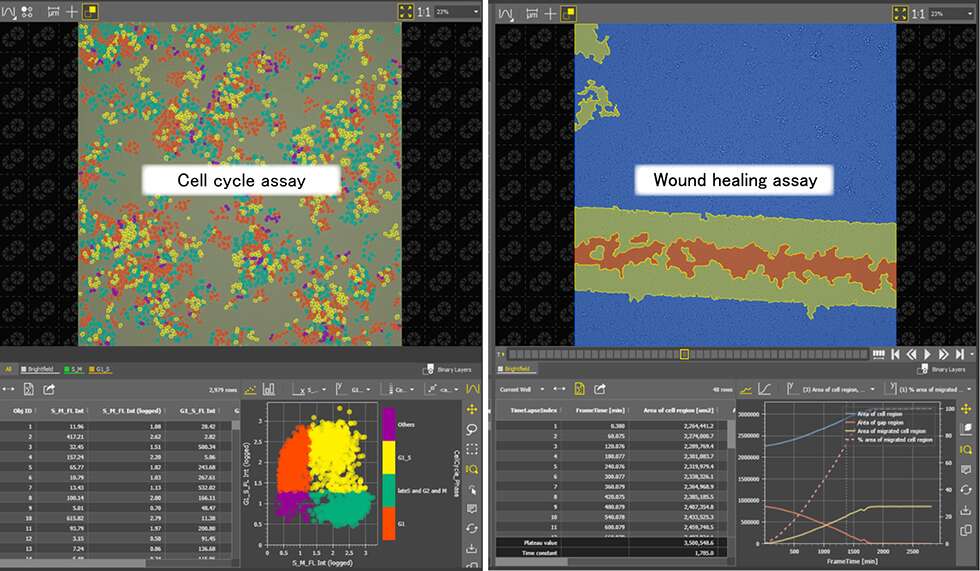
Right: Example of wound healing assay results (blue: cellular area, red: gap area, yellow: area of confirmed cell proliferation)
2. Streamlined neuronal morphology analysis for the study of neurological diseases
Neurons exhibit distinctive morphology, and their structure and function are closely related. The neurite outgrowth assay can, for example, automatically analyze the length and number of outgrowths to investigate the effects of drugs on neuronal morphology. Neuronal structure is typically a challenge to automatically analyze, and this new assay is expected to greatly improve the efficiency of neurological disease and regenerative medicine research.
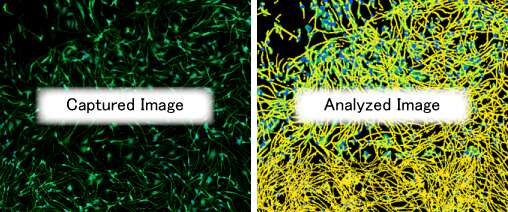
Left: captured image; Right: analyzed image.
Yellow: neurites, green: nerves, blue: nuclei, orange: number of branches
3. Improved time-lapse analysis, critical in capturing biological functions
To support research mimicking in vivo biological processes, a new time-lapse function has been added that allows observation of changes in living cells over time, such as changes in cellular morphology or the progression of intracellular damage. For example, the cell counting assay can now measure cell proliferation over time. In addition, new and enhanced graphical displays facilitate visual evaluation of the multi-dimensional results over time to support more complex studies.
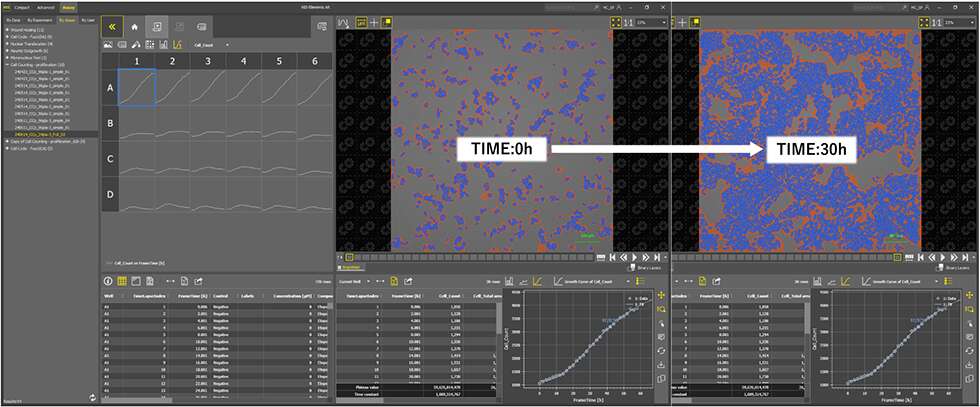
Left: data at the beginning of the experiment
Right: data at the final stage of the experiment
“In pursuit of cutting-edge technology that contributes to the development of science and technology, Nikon releases NIS-Elements ver. 6.10, the latest version of its software for the ECLIPSE Ji. This update combines user-friendly operation with high-precision analysis functions to significantly improve experimental efficiency, specifically for biotechnology companies, research institutes, and organizations that are conducting drug discovery research,” said Tatsuya Yamaguchi, Senior Vice President, General Manager of Healthcare Business Unit. “At Nikon, we continue to develop products that respond to the evolving needs of the drug discovery field with the overall goal of contributing to the improvement of the health and welfare of all people in society.”

